LIBRARY
A Double-Side Cooled SiC MOSFET Power Module with Sintered-silver Interposers
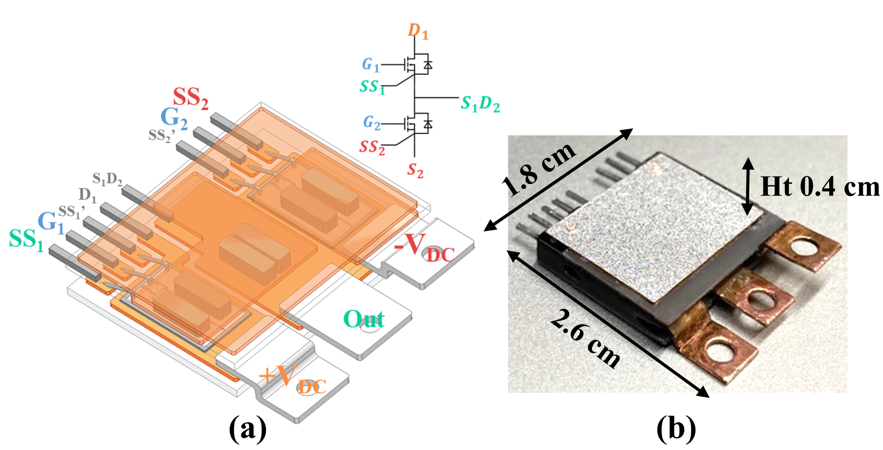
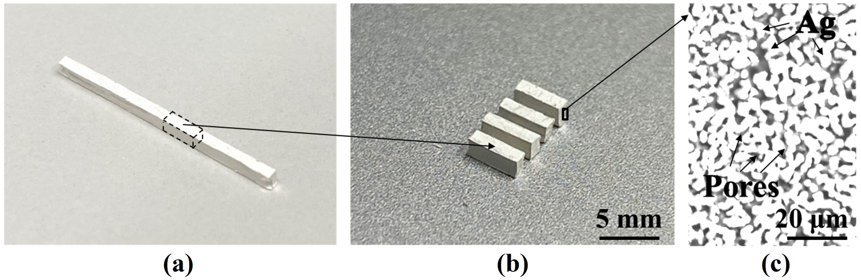
In this work, a porous interposer made of low-temperature sintered-silver (Ag) is introduced to reduce the thermo-mechanical stresses in the module. A double-side cooled half-bridge module consisting of two 1200 V, 149 A SiC MOSFETs shown in Fig. 1 was designed, fabricated, and characterized. The appearance and microstructure of sintered-Ag interposers are shown in Fig. 2. By using the sintered-Ag instead of solid Cu interposers, our simulation results showed that at a total power loss of 200 W, the thermo-mechanical stress at the most vulnerable interfaces (interposer-attach layer) was reduced by 42% and in the SiC MOSFET by 50% with a trade-off of only 3.6% increase in junction temperature. The sintered-Ag interposers were readily fabricated into desired dimensions without post- machining and did not require any surface finishing for die- bonding and substrate interconnection by silver sintering. The porous interposers were also deformable under a low force or pressure, which helped to accommodate chip thickness and/or substrate-to-substrate gap variations in the planar module structure, thus simplifying module fabrication. Experimental results on the electrical performance of the fabricated SiC modules validated the fabrication of a module design that employs the sintered- Ag interposers and all sintered-Ag joints for making high power-density converters with reliable operations at high junction temperatures.