LIBRARY
Reduced Order Modeling of Power Converters for System-level Studies
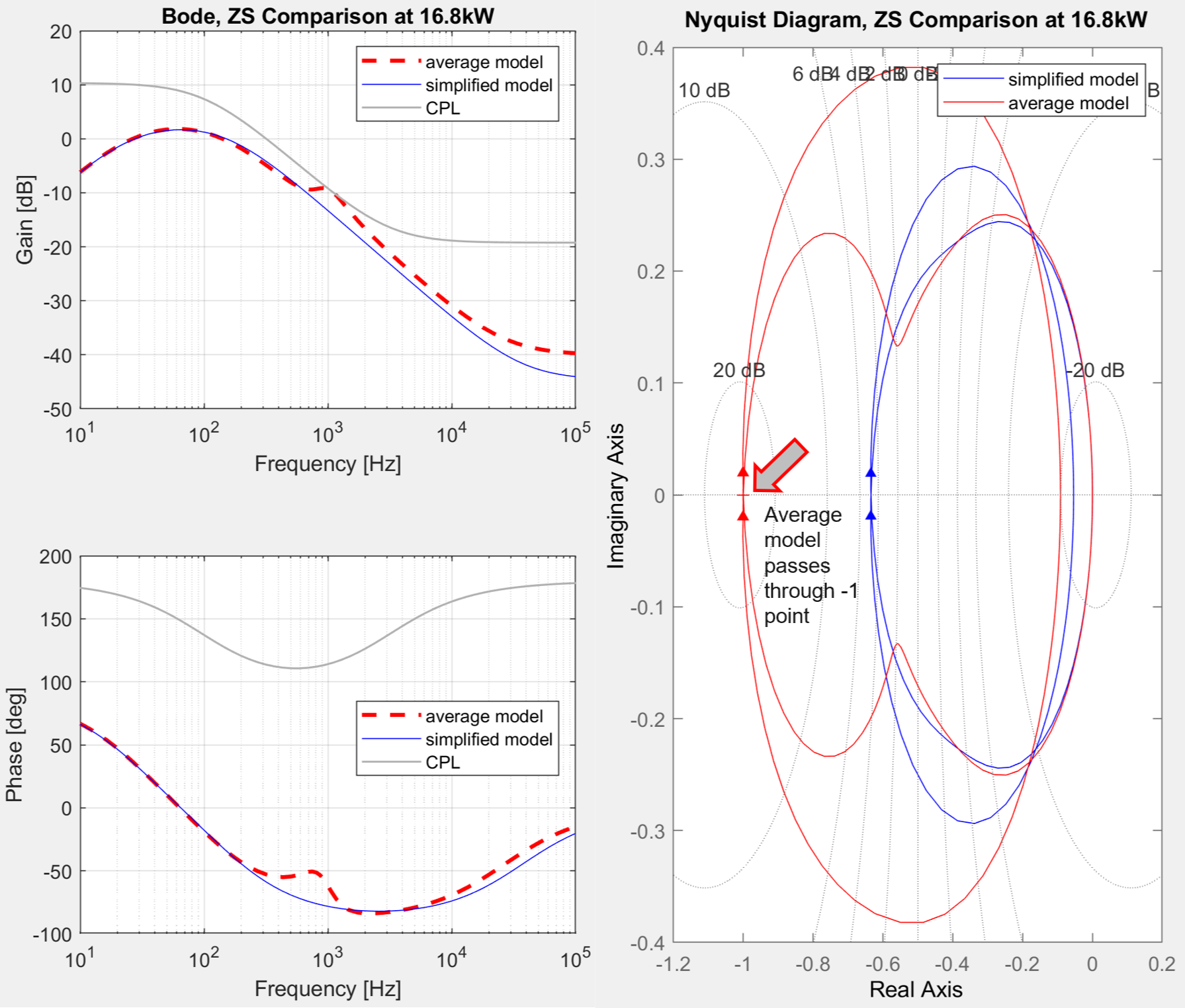
The challenge lies in analyzing the source-load impedance interactions. If a power converters higher-order source impedance transfer function curve contains salient points not represented in the reduced-order model, there may be cases where the source-load impedance interaction appears stable for a reduced-order model, but is revealed to be unstable by a higher-order average-value model. This may appear in the form of insufficient phase margin where the Bode gain plots intersect, and in the form of Nyquist encirclements of the -1 point. It is desired to determine if a correction can be included in the simplified model.
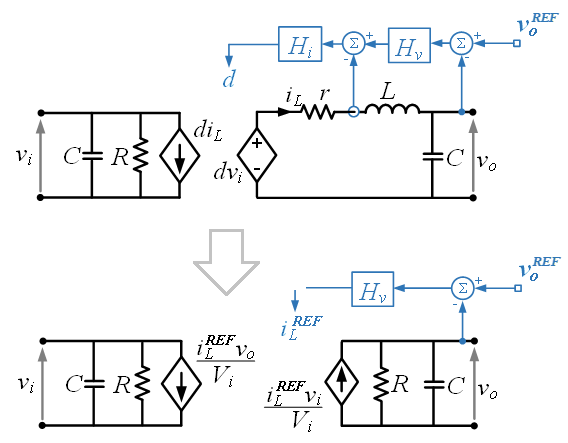
The simplified model of the characteristic 250 kW dc-dc buck converter was loaded with an identically structured converter representing a constant-power load of 15-30 kW. The source and load transfer functions were then extracted and manipulated to compare load-source impedance interactions for average versus simplified converter models, with a focus on the impact of any salient points in the gain and phase curves which are evident for the higher-order average model, but not for the lower-order simplified model.