LIBRARY
A Guide for Accurate and Repeatable Measurement of the RTH,JC of SiC Packages
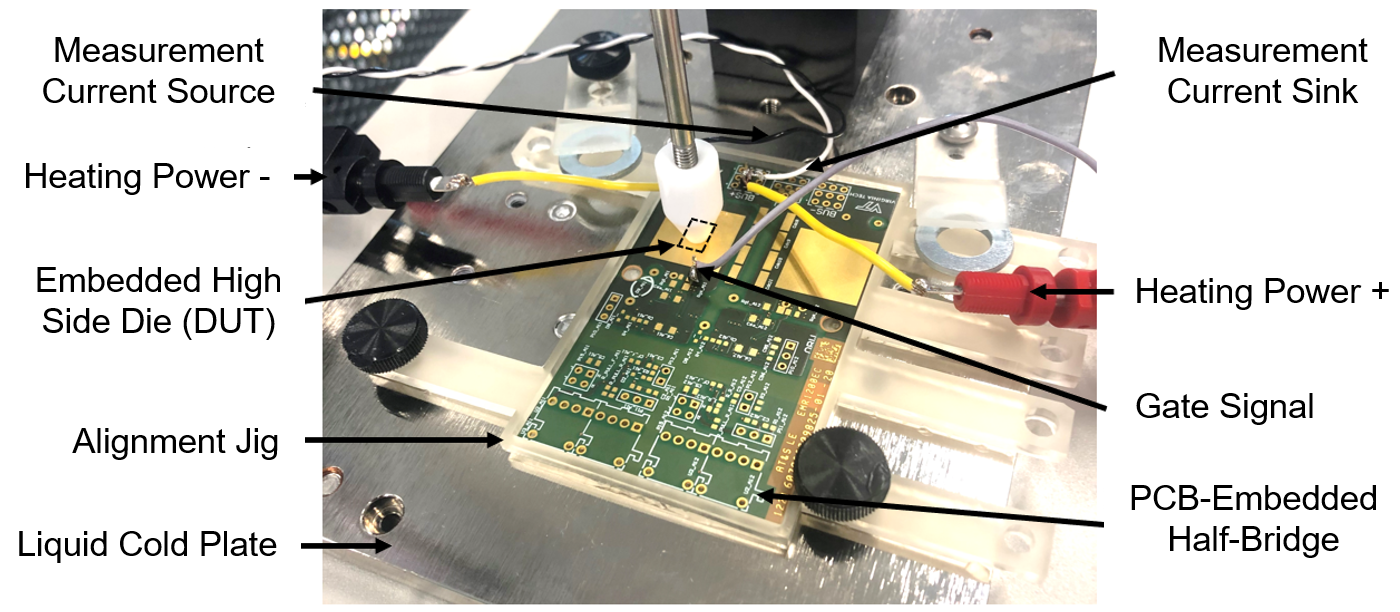
This work studied pressure, thermal grease conductivity, thermal grease thickness, copper standoff thickness, negative gate voltage applied during junction temperature measurement, and clamp tip style. Seven sets of 25 RTH,JC measurements were taken - one control set and six sets with one of the conditions listed above set to an alternate value. Fig. 2 illustrates a box and whisker plot of each set of RTH,JC measurements. Dow Corning TO-5026 (2.9 W/mK), the alternative to Dow Corning 340 (0.5 W/mK), has the lowest standard and maximum deviations. Since the Dow Corning TO-5026 has a higher thermal conductivity than Dow Corning 340, it tends to separate more from the silicone oil curve, creating a clearer divergence point that leaves less room for error to impact the RTH,JC determination.
Statistical analysis was required to determine the significance of the differences in RTH,JC mean between the sets of data. An analysis of variance (ANOVA) performed on the data provided sufficient statistical evidence to conclude that the different sets of test conditions have some effect on the measured RTH,JC; therefore, Tukey's honestly significant difference (HSD) method was able to be performed on the data. Tukey's HSD revealed that RTH,JC measurement sets resulting from alternative copper standoff thickness, negative gate bias, thermal grease thickness, and clamp tip style have statistically significant differences in the RTH,JC measurement mean compared to the control set.


















































































