LIBRARY
Loop Gain Modeling of a Single-Phase PFC for Online Small-Signal Stability Monitoring
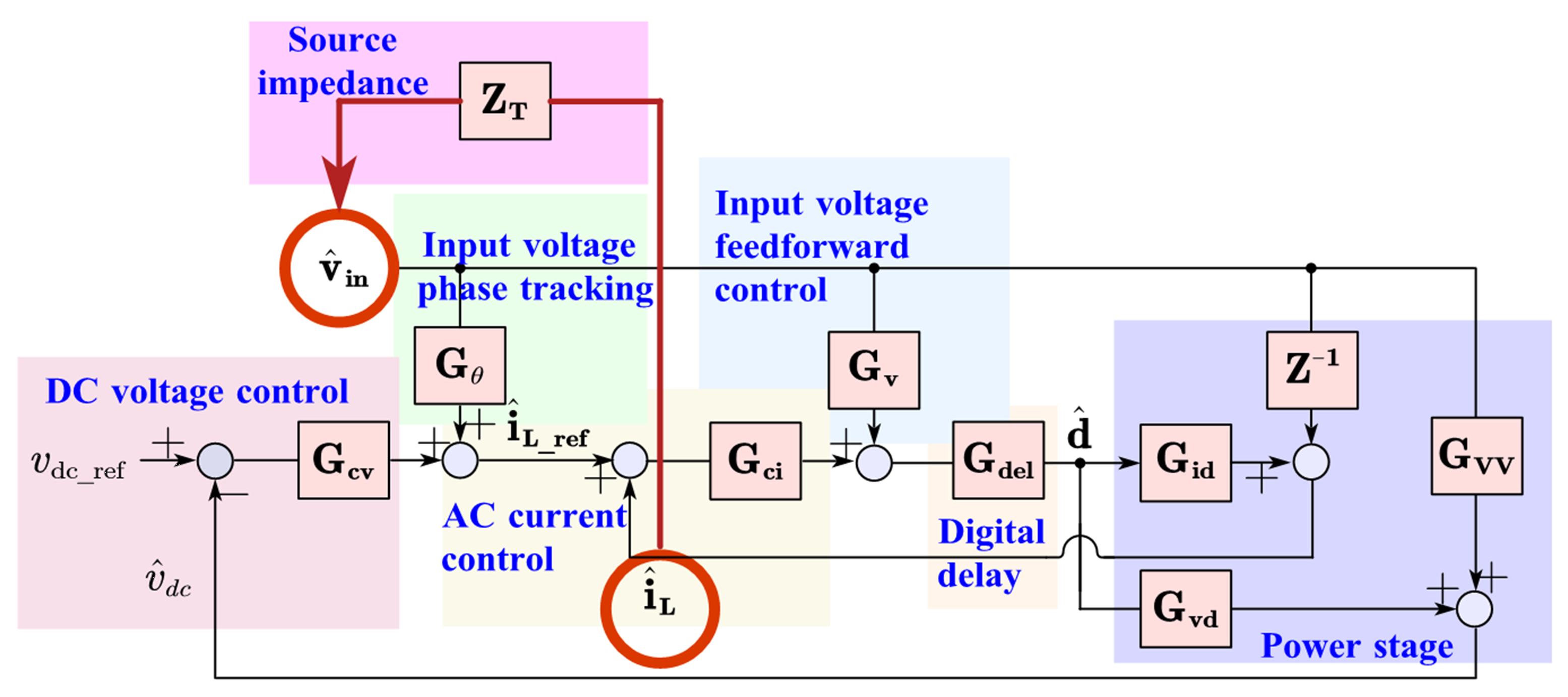
The basic idea of virtual d-q frame modeling for both a single-phase and a three-phase system is to create virtual frames by phase shifting the original systems, and transforming the artificial
three-phase-balancedsystem to another rotating frame, in which the system's operating points are time-invariant, so linearization and small-signal analysis are achievable. Fig. 1 shows the small-signal model of a single-phase PFC when considering the source dynamics ZT, including any source impedance or other PFC converters. ZT can be derived based on the system configuration and parameters, and works with either a single-phase system or a three-phase-four-wire system. Then the PFC voltage open-loop gain can be derived as follows:
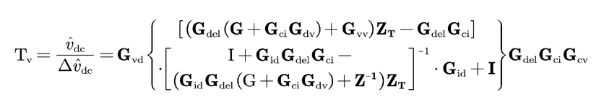
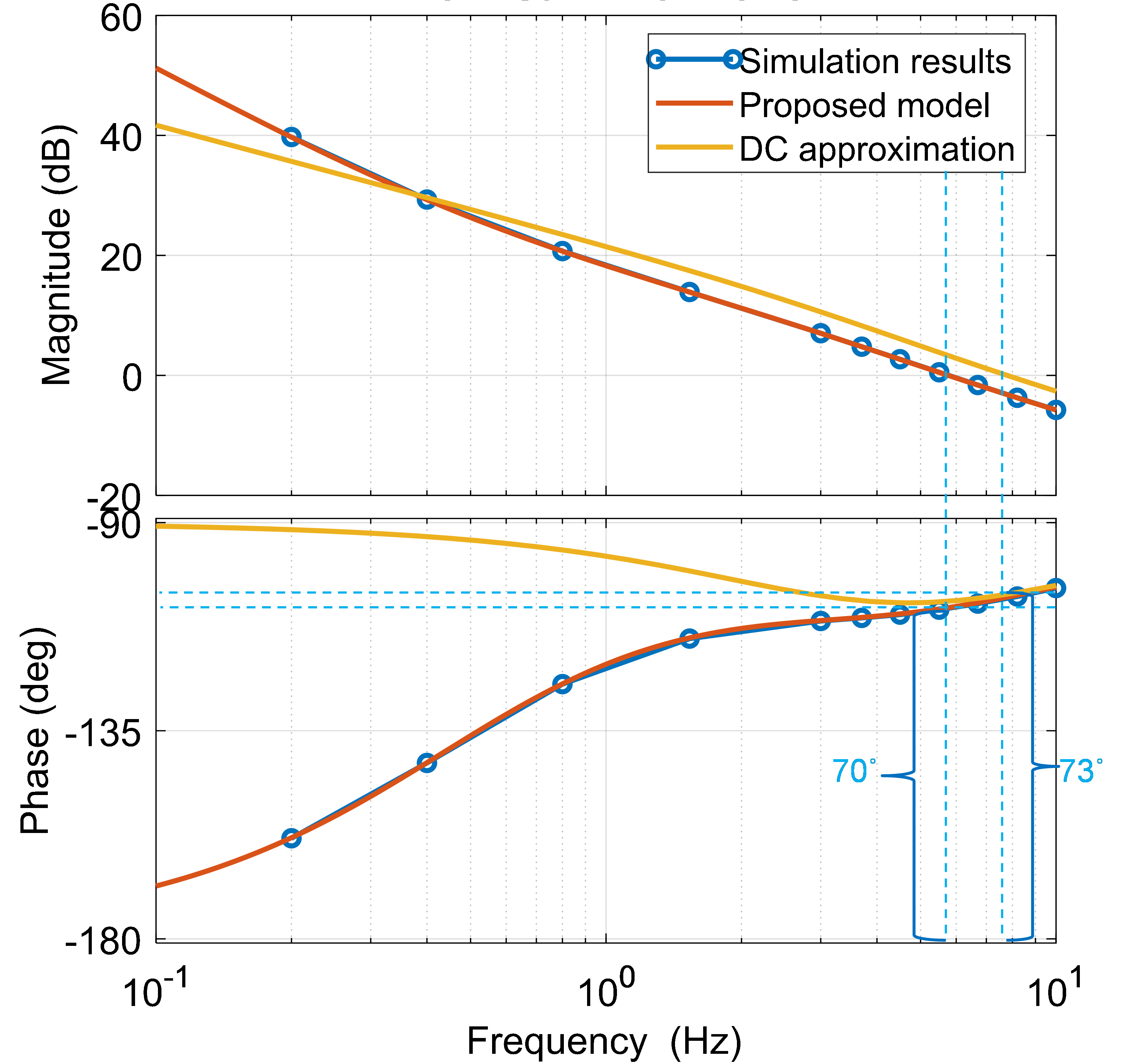
The conventional quasi-static approximation for modeling or measuring a PFC's voltage loop gain is done by approximating the PFC converter's dynamics as that of a DC-DC converter. The input voltage of the DC circuit is frozen to be the same as the RMS value of the AC input voltage of the original circuit. Fig. 2 (a) shows the simulation and modeling results for a single-phase system. The proposed model is much more accurate than the quasi-static approximation. Fig. 2 (b) shows the simulation and modeling results for a three-phase-four-wire system. The results of the proposed model closely match those obtained by simulation.