LIBRARY
EMI Mitigation for SiC MOSFET Power Modules Using Integrated Common-Mode Screen
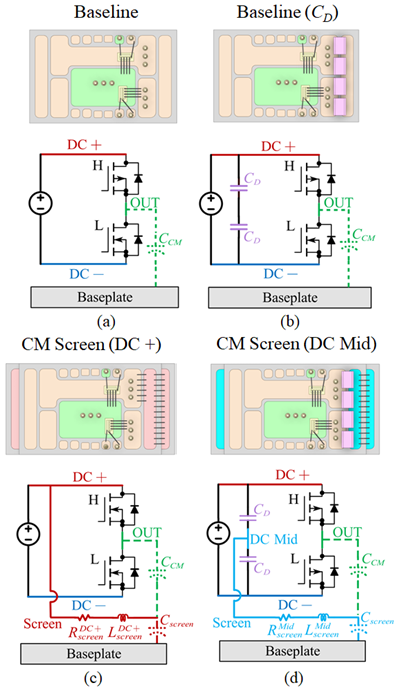
Four design variations (Fig. 1) were developed to study the impact of the module architecture on CM noise reduction. A second substrate layer was added into the module architecture to serve as a physical shield to redirect the noise generated by the switching node to the connected DC bus, reducing the current flowing through the baseplate. Two series decoupling capacitors were also included in two design variations to create the midpoint DC Mid. The decoupling capacitors reduce ringing during switching transitions, which results in lower noise being generated.
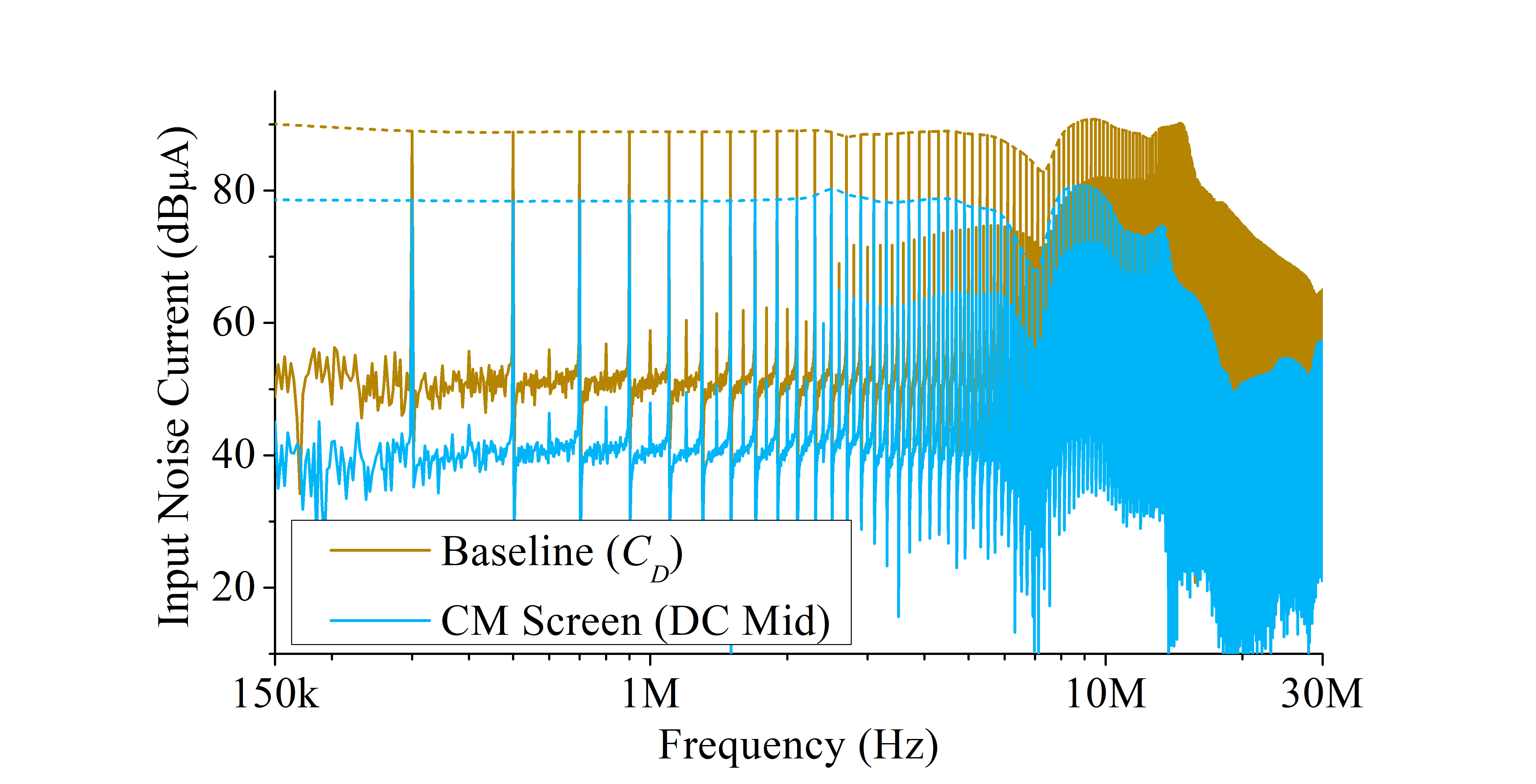
A test setup was developed to evaluate the level of noise mitigation introduced by the module architectures. The designed testbed switches each module as a buck converter operating at a switching frequency of 100 kHz, with input/output voltages of 600/300 V, and an output power of ~4.1 kW. The experimental results show that changing the DC node connected to the CM screen and the addition/removal of decoupling capacitors results in different mitigation levels and efficiencies. From the module architectures analyzed, the CM screen (DC Mid) module showed a current noise reduction of up to 26 dB compared to the Baseline (CD) (Fig. 2). The CM screen (DC Mid) module also showed a 0.5% increase in efficiency compared to a conventional module architecture (Baseline module).