LIBRARY
Improved Power Density of a 6 kV, 1 MW Power Electronics Building Block Through Insulation Coordination
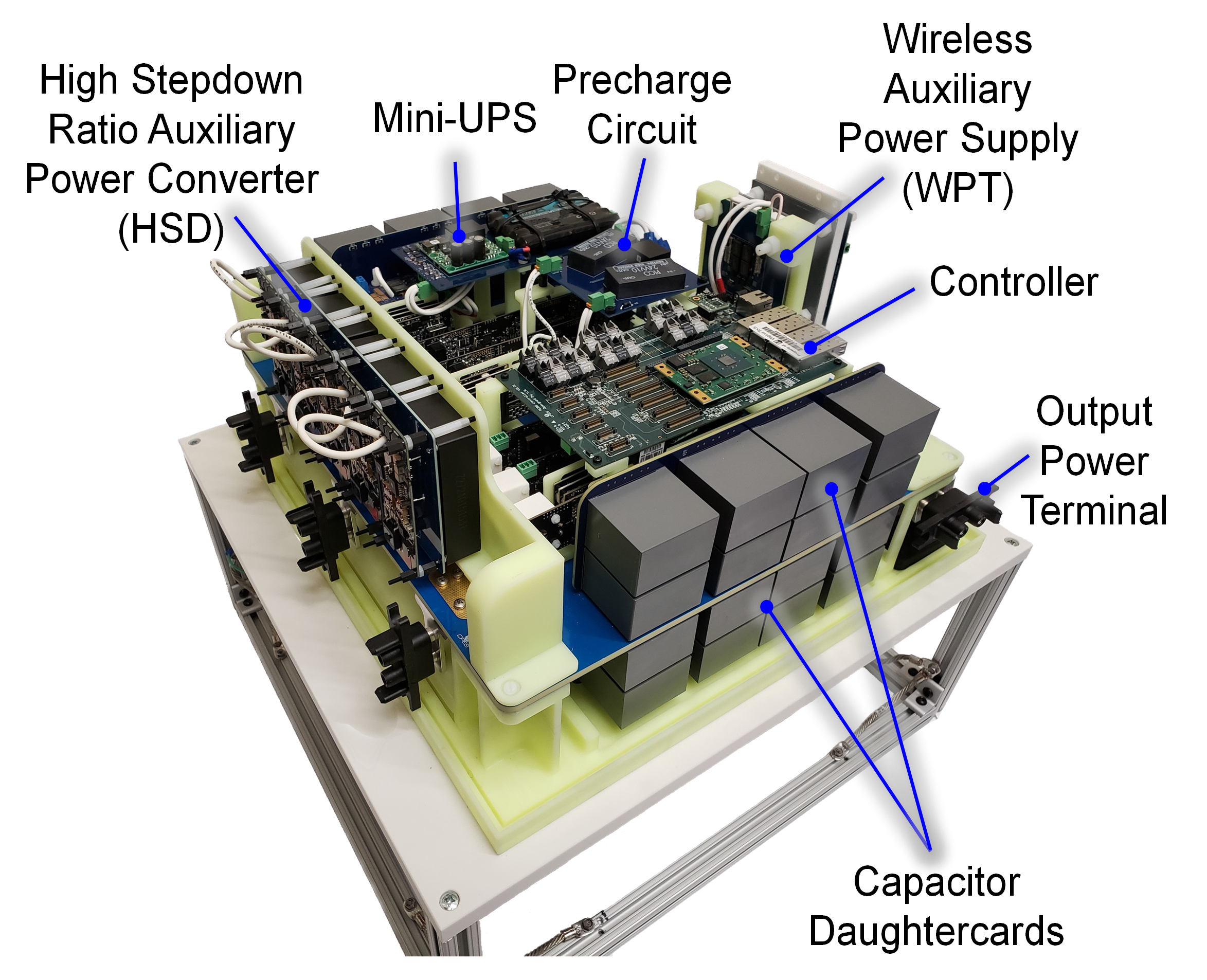
To maximize converter flexibility, the insulation system of each PEBB must be designed to withstand the maximum system voltage. In the case in which cooling fans are powered by earth-grounded power supplies, this voltage can exceed the converter's bus voltage. When using commercial components such as can capacitors, clearance requirements may increase between other components, which negatively impacts power density. Additional clearance must also be added to ensure reliability when routing high-voltage wires between components with a large differential voltage.
This work presents an H-bridge PEBB that incorporates all power stage components and ancillary circuitry. Finite element analysis (FEA) is used to extract parasitics and model the insulation in high-voltage regions. A medium-voltage dc (MVDC) bus is designed to integrate a low-voltage auxiliary power bus, which simplifies cable management. Medium-voltage (MV) capacitor daughter cards rated for 3 kV, 44 µF are designed to improve overall power density. A custom heatsink profile and corona ring are designed to reduce enhancements to the electric field (E-field) intensity. Insulation systems within the PEBB assembly that are subject to high E-field intensity are tested via partial discharge analysis to ensure reliable operation.


















































































