LIBRARY
Investigation and Comparison of Cascaded H-bridge and Modular Multilevel Converter topologies for Medium Voltage Drive Applications
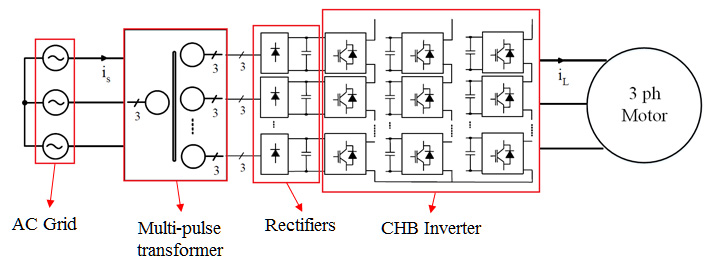
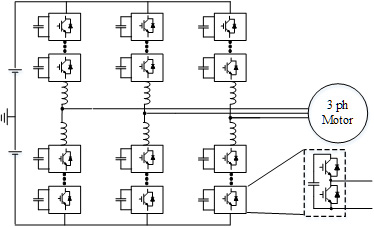
Fig.1 shows that the cascaded H-bridge converter (which is also known as Robicon converter) is composed of a multi-pulse transformer, 6-pulse diode front end rectifiers with a dc link filtering capacitor, and a cell-based inverter. The design procedure must include a specified procedure for determining the values and the selection of components for each of the mentioned parts.
In a similar way, the schematic of a modular multilevel converter (MMC) is brought out in Fig. 2, where the converter is composed of a series connected half-bridge modules and arm inductances. The dc links in the case of the MMC converter can be provided by an MMC rectifier or multi-pulse rectifiers.
The aim of providing design procedure is to design converters so we can compare the con-verters to each other from as many aspects as needed. Once we have both converters in hand, we may compare them from different points of view such as: number of parts (which affects reliability), individual component rating, energy storage, efficiency, power quality, controllability, modulation requirements, control requirements and maximum available output frequency.