LIBRARY
Efficiency Optimized AC Charging Waveform for the GaN Bidirectional PHEV Bat-tery Charger
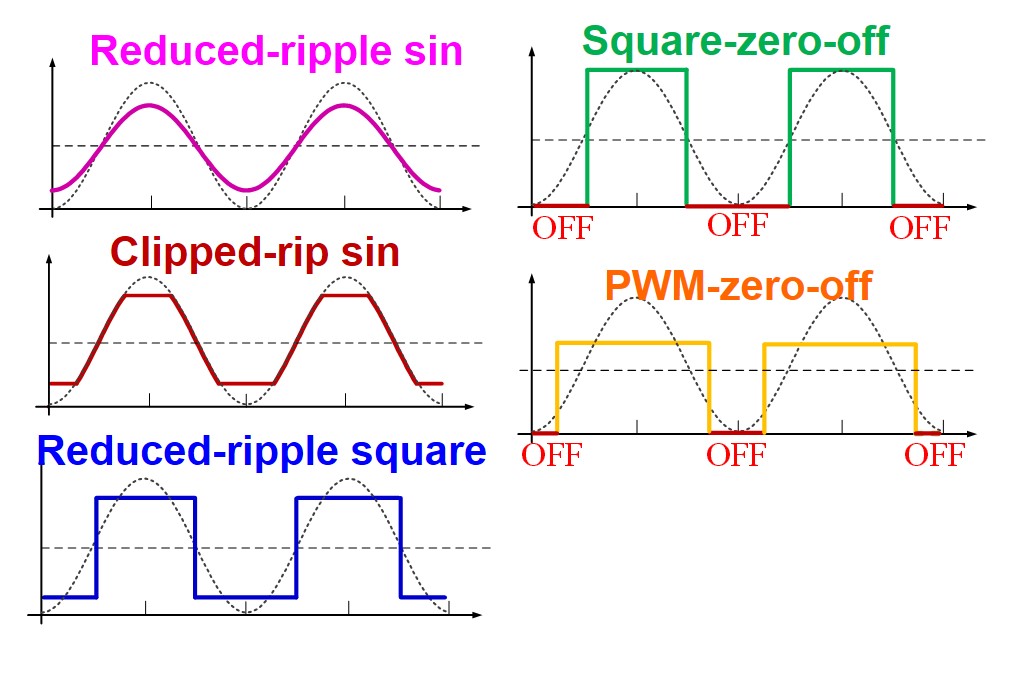
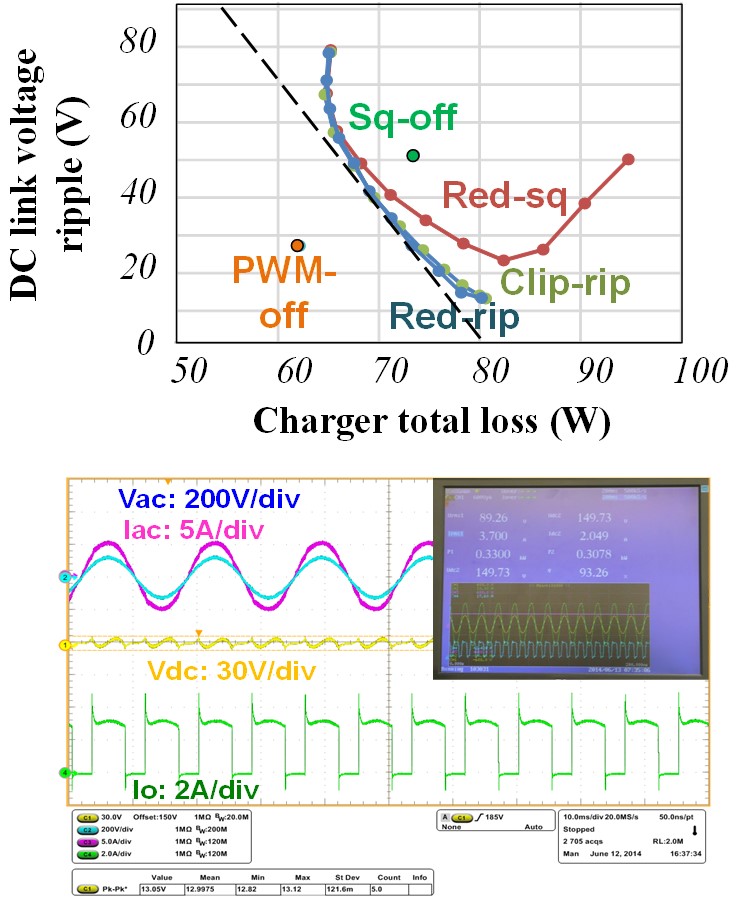
The waveforms under investigation are shown in Fig. 1. While all the waveforms should deliver the same average value, as determined by the charging profile, they can be divided into two categories. The left three waveforms have adjustable ripple amplitude, while the right two waveforms have fixed ripple amplitude. Since the charging current of the right two waveforms always touches zero, the DC-DC stage is turned off at the zero part of the output current, where, essentially, no power is delivered. For all of the five charging waveforms, we need to evaluate the converter efficiency and DC link capacitance requirements. Or, equivalently but more conveniently, we can evaluate the converter loss and DC link voltage ripple. The best charging waveform should give both minimum converter loss and minimum DC link voltage ripple.
The evaluation results are shown in Fig. 2. From the top figure, we can see that PWM-zero-off charging gives the minimum amount of loss and DC link voltage ripple compared with all of the other waveforms. The bottom chart shows the measurement waveform of a GaN-based battery charger. With PWM-zero-off charging, the charger saves 39% of converter loss with the same DC link voltage ripple, as compared to the second best charging waveform - reduced-ripple sinusoidal charging.