LIBRARY
Development of an Integrated DPS Front-End AC/DC Converter (1998-2008)
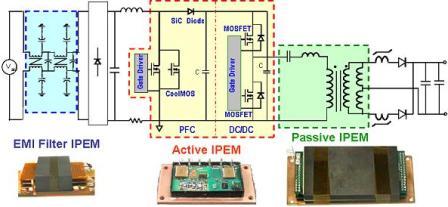
For the dc-dc converter, center researchers made significant efforts in evaluating various PWM converter topologies. Subsequently, researchers chose the asymmetrical half-bridge (AHB) among many other candidate topologies for the reasons of high efficiency and simplicity. Further improvements included: 1) asymmetrical transformer turns-ratio to increase the duty ratio when operated at 400 V input, 2) a range switch to reduce the transformer turns ratio during hold-up time and improve efficiency more than 2% at full load. Using the packaging of the active IPEM with wire-bonds, researchers demonstrated a prototype dc-dc converter that was used as a benchmark AHB dc-dc converter.
For the PFC converter, center researchers used the newly developed SiC diode and CoolMOSTM devices and showed a more than 35% loss reduction. This has enabled us to increase the PFC switching frequency from 100 kHz to 400 kHz, and to successfully demonstrate a twofold size reduction of the boost inductor and a 15% reduction of the EMI filter. Employing the circuit improvements mentioned above, researchers demonstrated a prototype with 30% reductions in both profile and footprint with 7.5 W/in3 power density. This particular design was used as a baseline design for developing an integrated converter with integrated active and passive IPEMs.


















































































