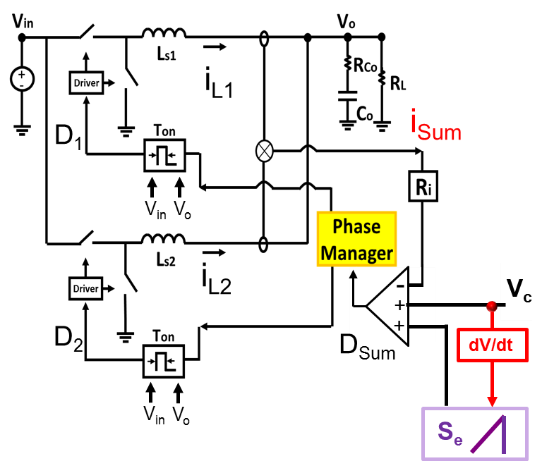
Fig. 1. Proposed variable ramp COTCM structure by adding dVc/dt with conventional ext. ramp.
Constant on-time current mode (COTCM) control schemes are widely used in the industry for their light load efficiency, higher BW design with simpler compensation requirement and better transient performances. In a COTCM multiphase operation, the summation of all phase inductor current (I
sum) interacts with a voltage loop compensator output (V
c) to generate the duty cycle. The issue with this method is that when duty cycle approaches the 'ripple cancellation point' (e.g. D=0.5 for 2-ph operation) this inductor current summation (I
sum) becomes increasingly smaller. In that case, control becomes very noise sensitive and output shows jittering. Normally an external ramp (S
e) is added to the modulator to reduce this jittering and higher value of ramp will reduce the jittering. But unfortunately with the increment of the external ramp value, although the jitter in the system gets reduced, the transient performance becomes worse. Moreover, the system bandwidth also decreases with the increment of external ramp, which eventually slows down the transient response even more. For these reasons, from a transient point of view, it is very challenging to use a large external ramp in the system to reduce jittering. In this paper, a novel method is proposed to modify the external ramp at the transient instant to improve the transient response (by increasing the slope of the ramp), and thus allow the control to use the large external ramp for noise performance improvement and enjoy the fast transient response at the same time.
In Fig 1, the proposed structure where the derivative of V
c to increase the ramp slope in transient, is added with the conventional COTCM structure. In conventional COTCM in Fig 2a, we can see that with the large external ramp, the V
c and I
sum distance is very large in the steady state. Therefore, at the load transient it becomes very difficult for V
c and Isum to cross each other, which prohibits the duty cycle from saturating in order to increase the inductor current quickly. In Fig 2b, we can see that when a heavy load transient occurs, the dV
c/dt is added with the slope of the external ramp, which is shown by a green circle in Fig 2b. As the slope becomes very high at transient, the duty cycle also becomes very high very quickly in order to increase the inductor current which reduces undershoot at output. Comparing Fig 2a and 2b, we can clearly see that, output voltage undershoot can be reduced by using the proposed method. The main advantages of this method are, since we have used dv/dt of V
c, the detection is fast and optimum which will reduce any chance of ring back. In this method there is no threshold detection and the small signal property is not affected by the proposed method. By using the proposed method, COTCM control can have both a high noise performance and a fast transient performance together.
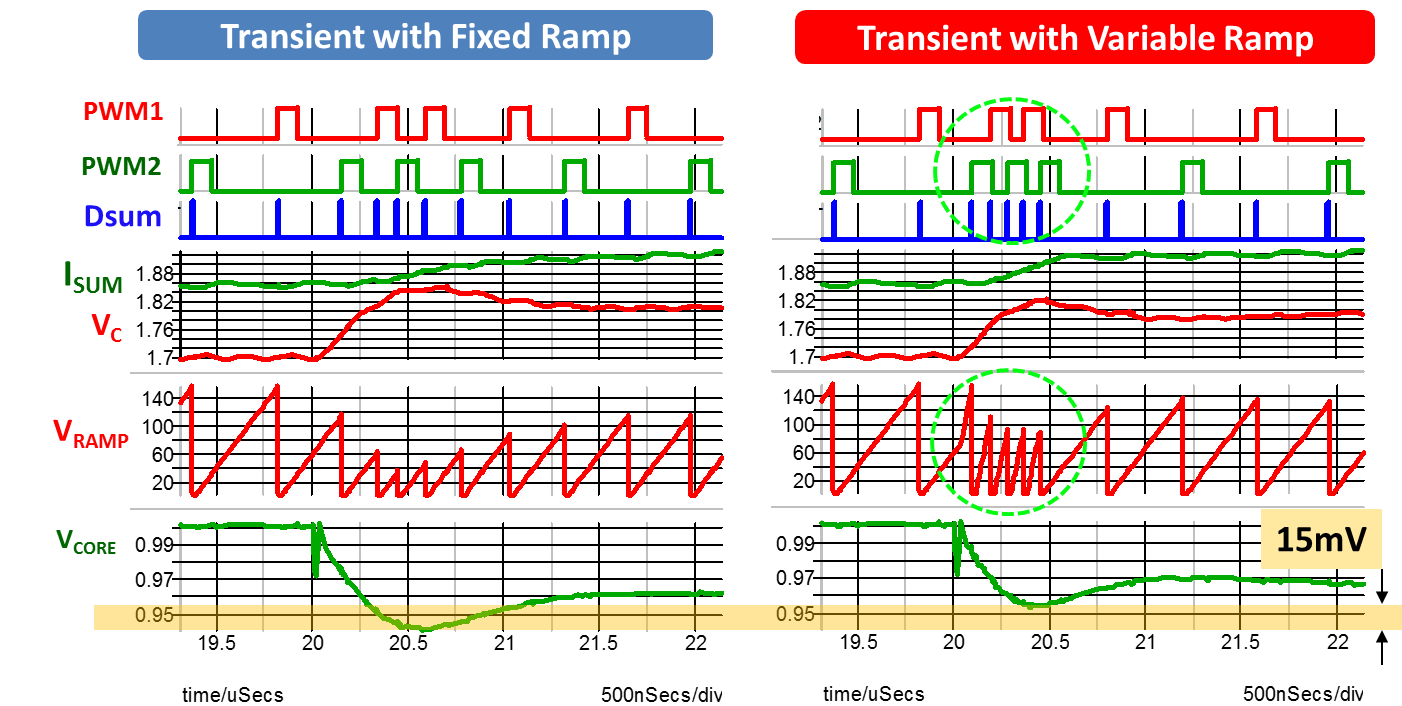
Fig. 2. (a) Transient response of COTCM with fixed ramp. (b) Transient response of COTCM with proposed variable ramp at transient.





















































































