RESEARCH
Two Comparison-Alternative High Temperature PCB-Embedded Transformer Designs for a 2 W Gate Driver Power Supply
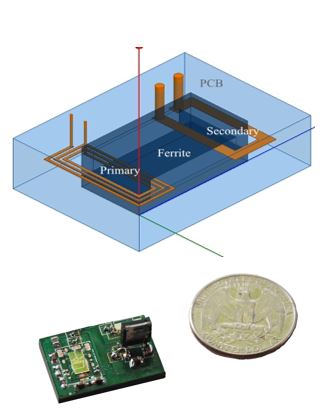
Two different transformer designs, the coplanar-winding PCB embedded transformer and the toroidal PCB embedded transformer, are presented and compared, as shown in Fig. 1 and Fig. 2 respectively. Both designs are dedicated to a 2 W gate drive power supply for wide-band-gap device, which can operate at 200°C ambient temperature. The former uses a 'C I' core and PCB winding within the core, which enables a far distance between the primary and secondary windings. Thanks to this structure, the co-planar transformer achieves 0.8 pF inter-capacitance. With the switching device located on the transformer surface, the final converter with 1 MHz switching frequency has a 74% overall efficiency at 2 W output power and its volume is 23 mm x 18 mm x 2.8 mm.
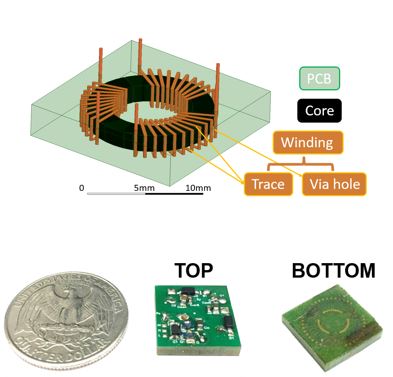
The secondary transformer is called the toroidal PCB-embedded transformer, where the core is toroidal and its windings are twisted around the core. With an optimization on the core size and winding size parameters, a targeted small inter-capacitance, a small transformer loss, and a small total volume, the transformer has a 1.6 pF inter-capacitance allowing the corresponding converter to achieve an 85% efficiency with a 1 MHz switching frequency and a total converter volume of 13 mm x 13 mm x 2.4 mm. The corresponding power density is 72.6 W/in3.