LIBRARY
Analysis of Phase-Locked Loop Low-Frequency Stability in Three-Phase Grid-Connected Power Converters Considering Impedance Interactions
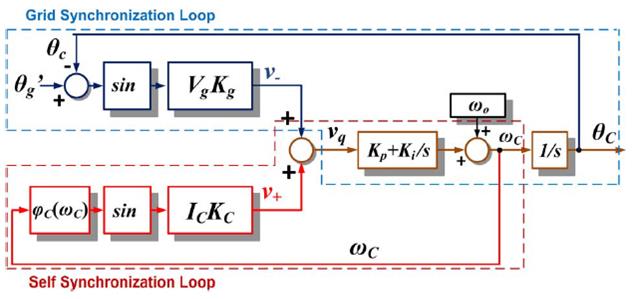
Fig. 1 shows the proposed PLL model considering the operation of the converter system. It is found that the effect of this self-synchronization feedback is determined by φC, IC, and KC. Higher injection current, bigger grid input impedance, and bigger reactive components (bigger φC) give a stronger self-synchronization feedback effect. In addition, the resonant frequency ωr is one of the PLL equilibrium points under islanded conditions. The corresponding linearized small-signal model shows that when the islanding condition occurs, the PLL output tends to approach ωr and to stay at ωr even with a perturbation.
It is also found that the "self-synchronization" feedback in the proposed model tends to drive the PLL output out of the steady state, and the loop characteristics greatly rely on multiple system parameters. The unstable nonlinear PLL output under the weak grid can be well predicted by the proposed model. A small-signal model under islanding conditions, derived from the quasistatic PLL model, clearly explains the LHP and RHP pole characteristics for parallel RLC and series RLC loads. Both simulation and experimental results have validated the proposed model, as shown in Fig. 2.
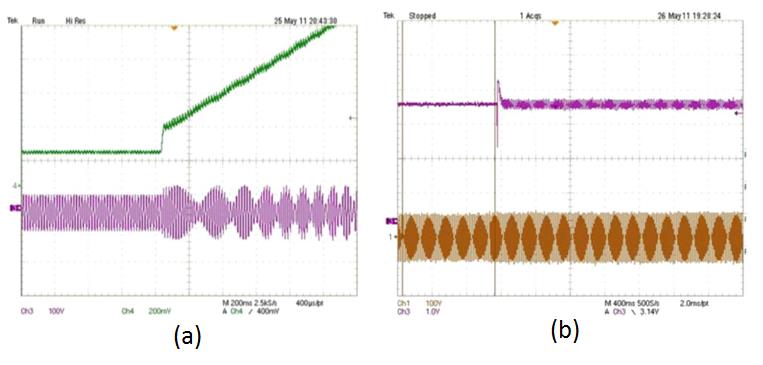
(b) PLL output under //RLCLLL load condition: phase voltage vCa (bottom) [100 V/div] and ωC (top) [5 Hz/div].




























































































