LIBRARY
Fault Characteristic Analysis in 56 Bus Distribution System with Penetration of Utility-scale PV Generation
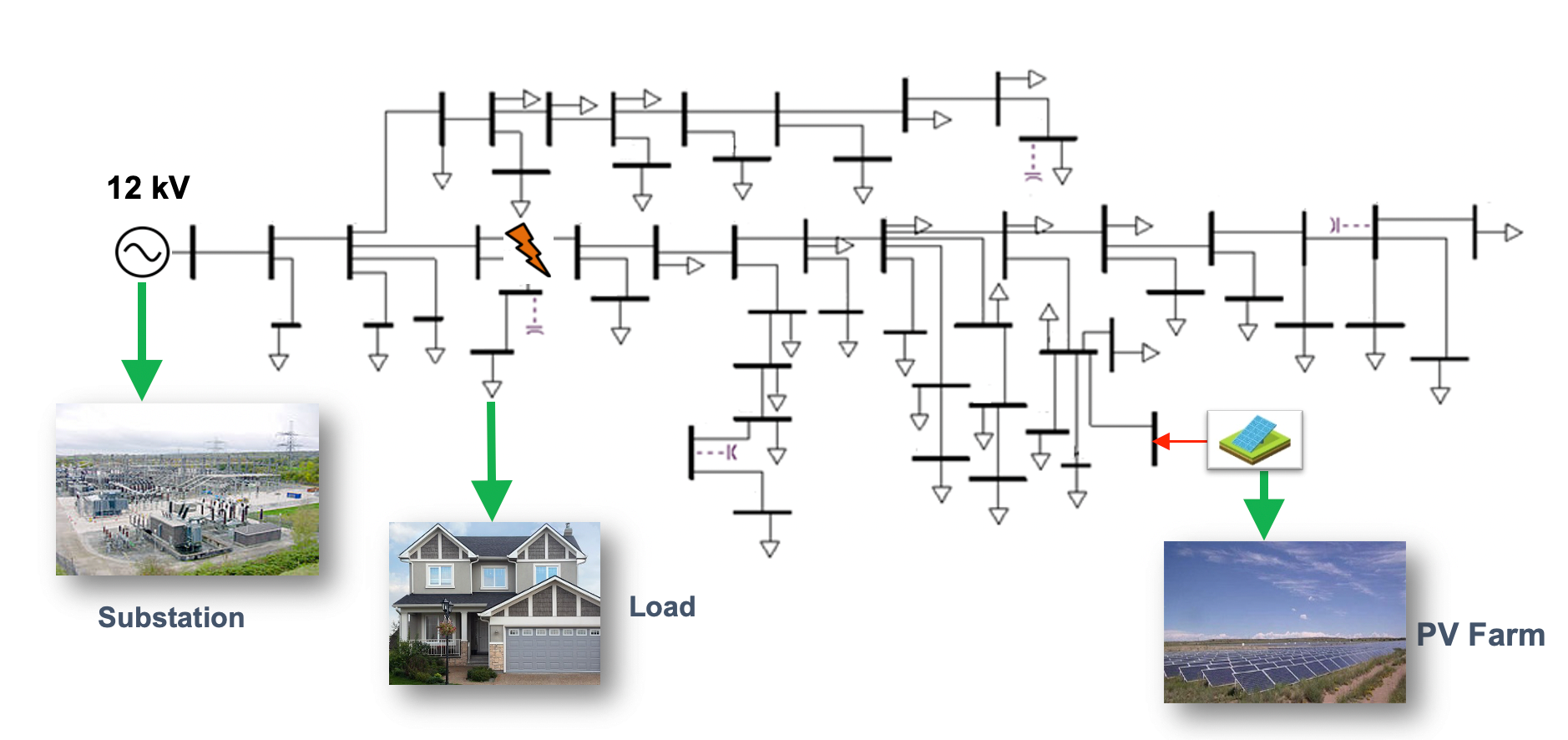
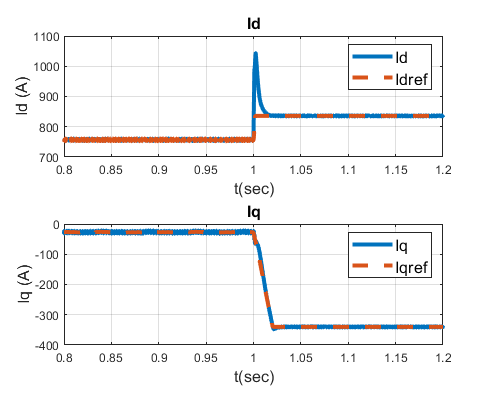
A 56-bus, light-loaded radial distribution system connected with a utility-scale PV farm as shown in Fig.1 was simulated in PLECS for fault analysis. The PV inverters control schemes are designed according to requirements stated in IEEE Standard 1547-2018. PV inverter fault performance and distribution system fault response are analyzed for both three-phase and single-phase short circuit faults, under different fault resistance and at different locations. After a short circuit fault happens in the distribution system, the PV inverter output current will only have a small increase because the reactive power control loop and dc voltage control loop both lose their effect. The current reference values on d and q axis will both hit their saturation limits while the current loop is still able to track the reference values, as it shows in Fig. 2. During a three-phase fault at PV upstream, most part of the PV output current will flow from the PV farm to fault, the relay at fault downstream and closest to the fault might incorrectly operate since its operation time could be set smaller than its upstream relays. The smaller the fault resistor is (or the closer the fault location is to the PV farm), the fault downstream current will be higher. For single phase fault at PV farm upstream, the PV output current and the fault downstream current at faulted phase is higher compared to three-phase fault case, which is more likely to cause the incorrect operation of fault downstream relay.
Based on simulations implemented on PLECS platform, this paper studies the impact of inverter-based solar photovoltaic (PV) source to a 56-bus distribution system and analyzes the distribution system characteristics under various different short-circuit fault conditions. The potential issues in system protective relays caused by DER penetration are also presented.