LIBRARY
Design of a PCB-Based Common-Mode EMI Filter of a 100 kW SiC Inverter for High-Altitude Application

Cables and toroidal cores are always used in the traditional common-mode (CM) chokes. However, the E-field is difficult to be controlled using the convection material and structure. Also, the inefficient heat dissipation and the bulky size prevent the application of the convectional CM choke. The planar core and PCB based CM choke is good for the control of the E-field and heat dissipation.
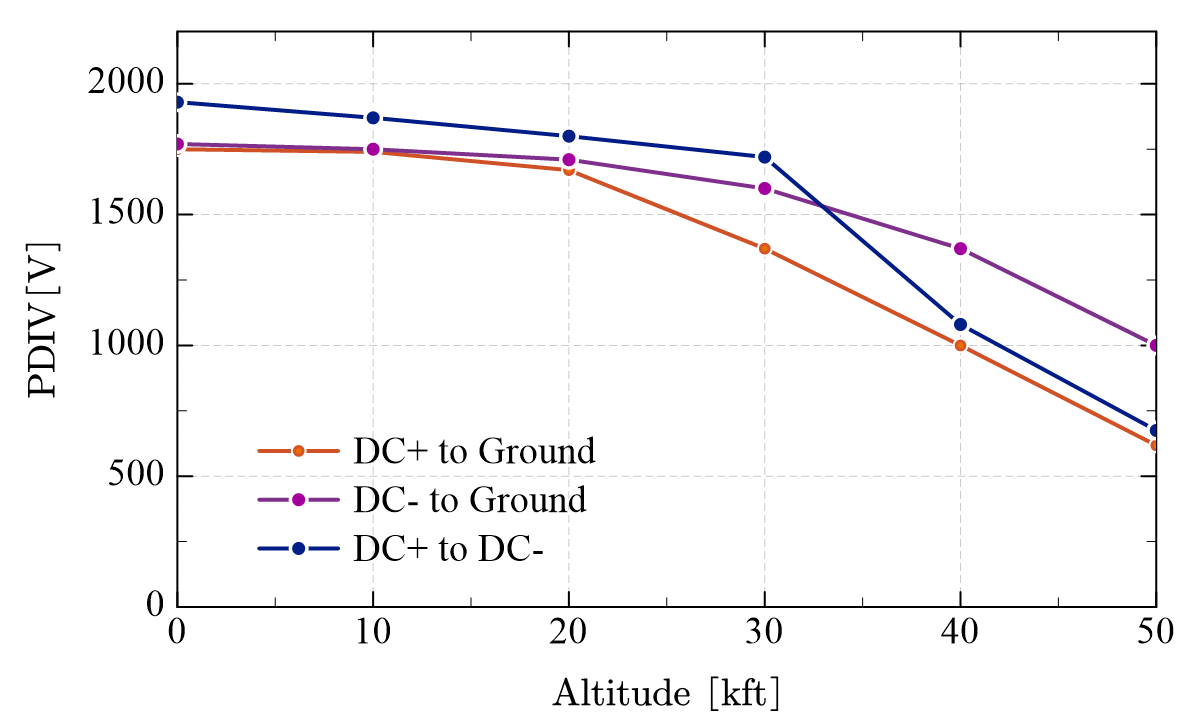
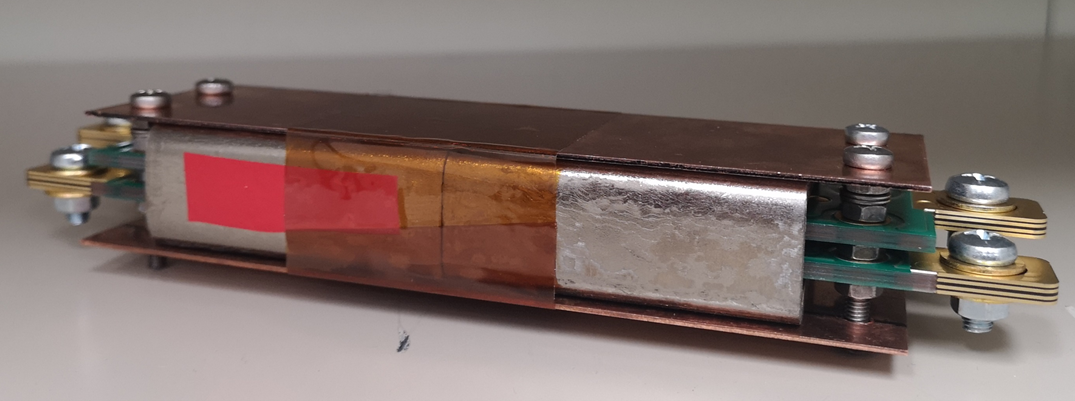
In this work, a PCB-based planar CM EMI filter of a 100 kW SiC inverter for high-altitude application is designed, as shown in Fig. 1. The CM model of the inverter system is analyzed, and a LC CM filter is designed based on the model. The dimensions of the core of CM choke are optimized to minimize the volume with the constraint of the E-field and heat dissipation at the altitude of 50,000 ft. To reduce the profile of the CM choke and control the electric field effectively, the PCB windings are adopted for the CM choke. The electric field of the CM choke is analyzed, and the PCB windings are designed to avoid PD at high altitude. Some grounded shielding traces are inserted into the PCB windings to reduce the risk of PD. The CM choke is tested in the 100 kW SiC inverter system and the PD test is conducted in the low-pressure chamber. The tests show that the CM EMI noise is reduced effectively with the CM choke and no PD occurs in the CM choke even at an altitude of 50,000 ft. The partial discharge inception voltage (PDIV) at different altitudes are measured, as shown in Fig. 2. The PDIV decreases as the altitude increases and PD does not occur even at the altitude of 50,000 ft.