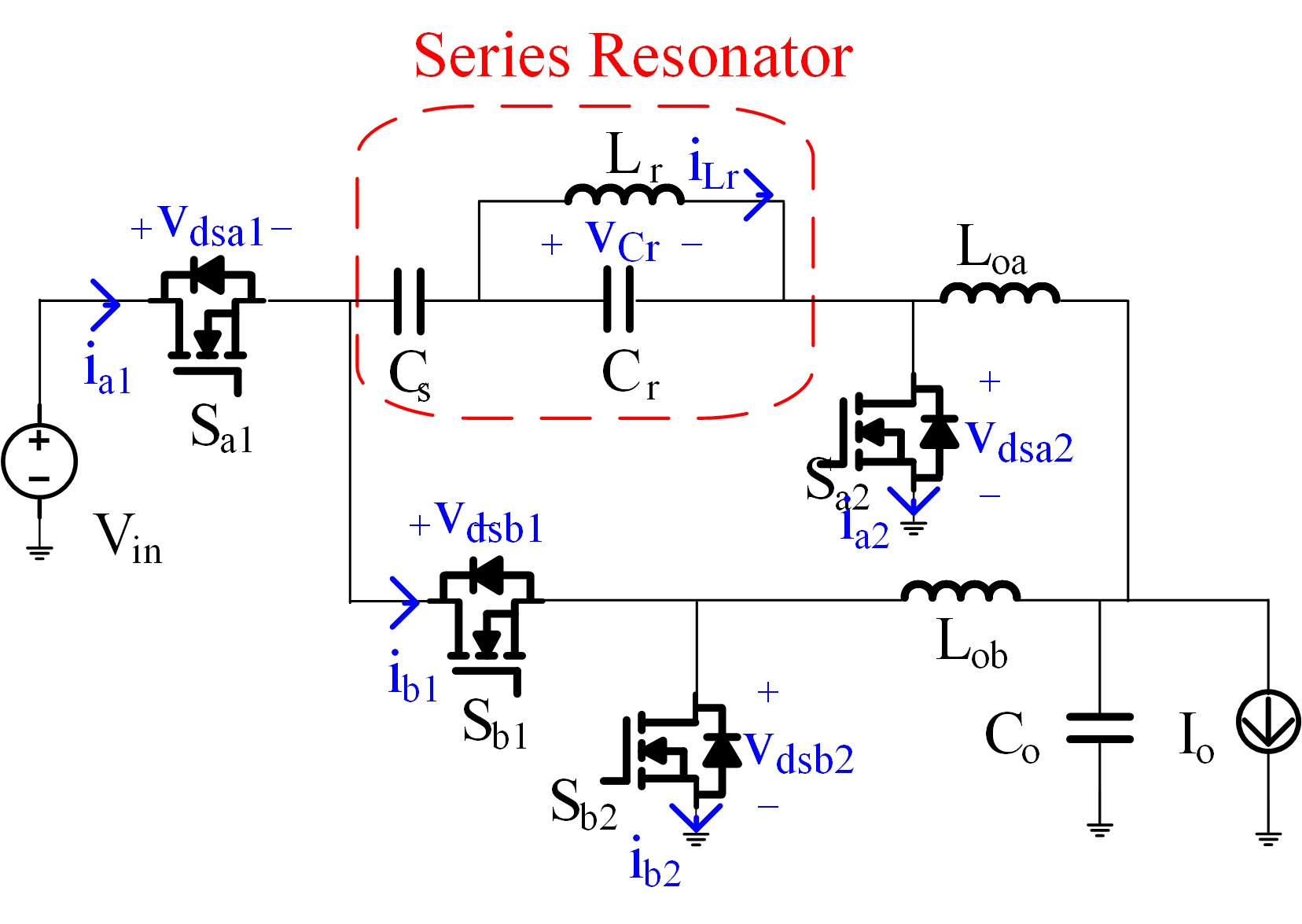
Fig. 1. Series-Resonator Buck (SRB) converter.
Interleaved multiphase buck converters have been adopted for point-of-load regulation below 3.3 V and above 10 A from input voltage exceeding 12 V. The Series-Capacitor Buck (SCB) converter was synthesized by adding a series capacitor in a two-phase buck converter to reduce voltage stresses under steady state. Side benefits include doubling of the duty cycle, reduction of the switching loss, and equalization of the phase currents. Hard switching has hindered efforts to reduce volume via increasing the switching frequency, although monolithically integrated SCB converter has boosted current density exceeding 60 A/cm
3 in. The efficiency dropped by 5%, owing to the switching loss, as the frequency increased from 1 MHz to 3 MHz.
The Series Resonator Buck (SRB) converter is synthesized by adding a parallel resonant tank next to the series-capacitor Cs, as demonstrated in Fig. 1. All switches turn on into zero-voltage (ZVOn), and low-side switches turn off from zero-current (ZCOff). No snubber is needed to keep the switches stresses within the input voltage. A 2-MHz prototype with 48 V at the input, and 7 V, 20 A at the output, was built to verify the design.
The peak efficiency of the RSCB prototype is 98.5%, and the full load efficiency is 97.3%, as shown in Fig. 2. The measured drain-source voltages of all switches at nominal condition are shown. All switches turn on into zero-voltage.
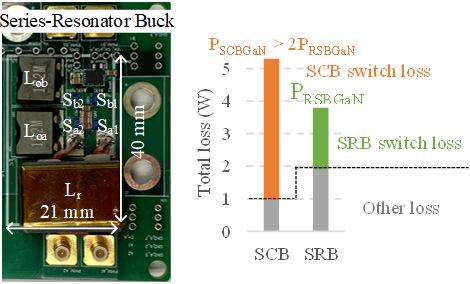
Fig. 2. Prototype and loss reduction compared with a conventional SCB converter
,




















































































