LIBRARY
An Isolated Constant-Current ZVS Class-E Inverter with Integrated Input Inductor
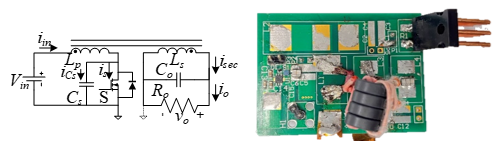
These drawbacks are overcome by the introduction of two coupled inductors, which integrate the two original inductors and a transformer (which would have been needed for grounding the load or for galvanic isolation). Interestingly, even though a transformer is incapable of stepping up the power, the maximum power of the improved inverter is boosted by the effective turns ratio of the coupled inductors. The duty ratio remains the same (0.5), and the switch's voltage stress is essentially constant. A design procedure is suggested for the integrated magnetics and is demonstrated by a prototype with 23.6W output power over a 24:1 output power range. Zero-voltage switching (ZVS) is maintained and the output current is constant within the output power range.


















































































