LIBRARY
Scalable Auxiliary Power Supply Architecture for SiC-based Medium Voltage Converter Systems
To develop a high-performance APS network for the safe operation of the switching devices, a few aspects need to be considered. First, the APS system must maintain stable, accurate, and independent output voltages for all auxiliary loads under various load conditions during normal operation, and is fault immunity. In the case of a system failure, an adequate insulation level is required, since the APS normally acts as the insulation barrier of the MV converter. Furthermore, a small isolation capacitance between input and output is preferred to reduce the common-mode current caused by high dv/dt in the system. Lastly, a simple and compact APS design is always desired.
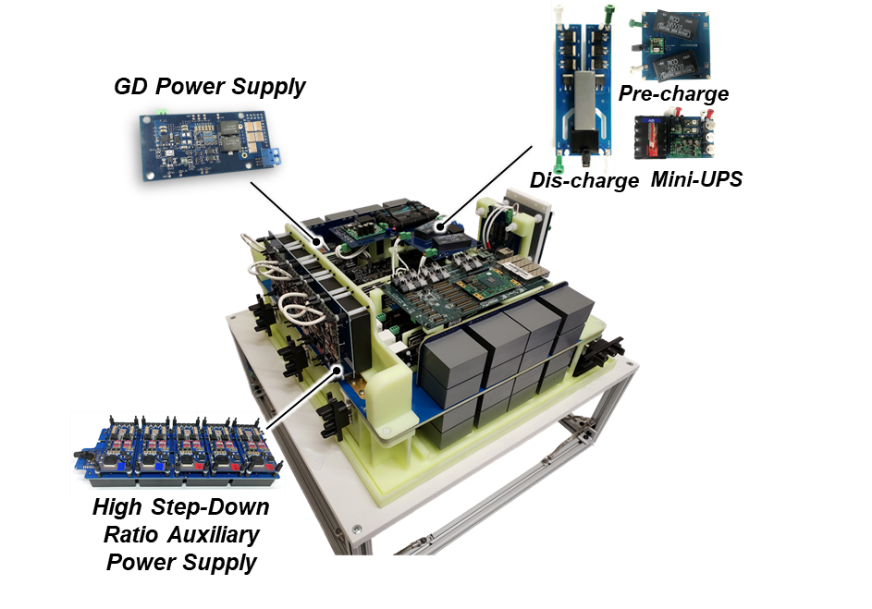
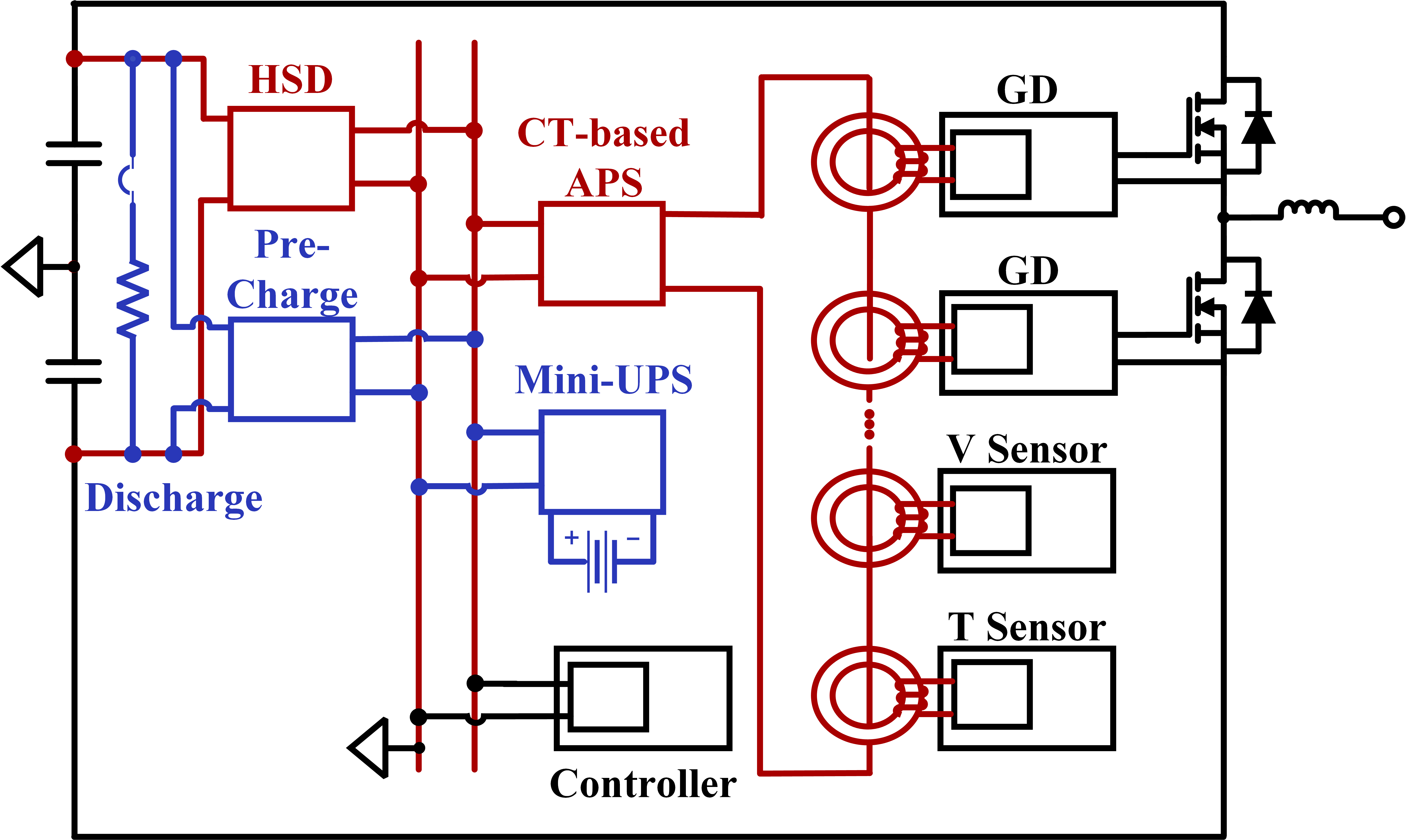
Therefore, to satisfy these requirements, an APS system is proposed, as shown in Fig. 1 Five converters including a high-step-down (HSD) converter, current-transformer-based auxiliary power supply (CT-based APS), pre-charge circuit, discharge circuit, and mini-uninterruptible power supply (UPS) are developed. The completed APS system gains power from DC-link capacitors in the MV converter, supplies the distributed loads simultaneously, and provides backup and start-up power. Overall, the proposed APS system is a modular design that has internal power capability, low insulation voltage requirements, high reliability, and low coupling capacitance. The assembled MV converter is presented in Fig. 2 with the APS system indicated.