LIBRARY
Magnetic Characterization Technique and Material Comparison for Very High Frequency IVR
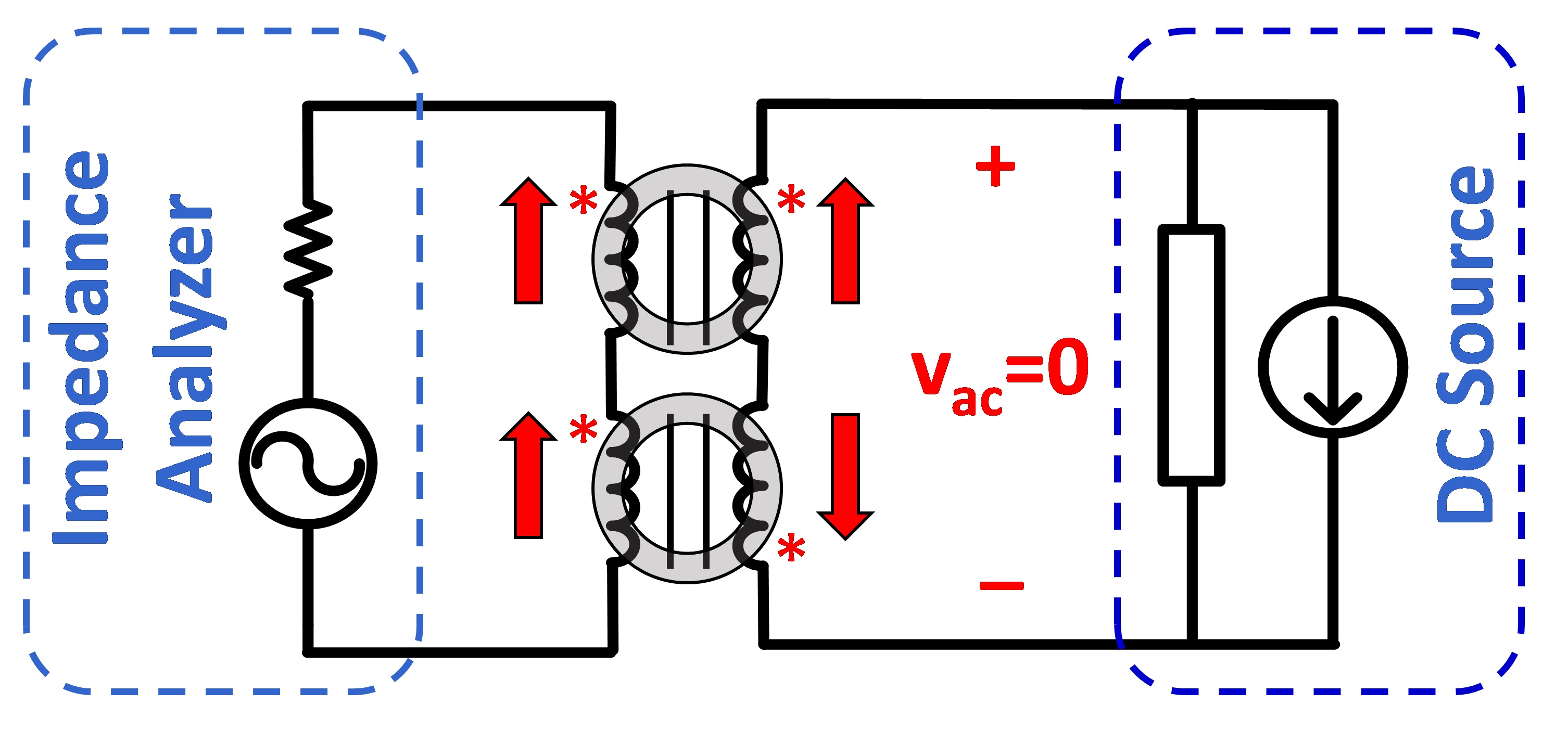
Fig. 1 shows an improved permeability measurement setup based on an Agilent 4294A impedance analyzer. The impedance analyzer has only 0.1A internal DC bias ability, which is not adequate to provide the required DC bias level for the core under test. Therefore, an external DC source is added. Meanwhile, an AC voltage cancellation mechanism is also implemented to diminish the error induced by the impedance of the DC source.
Fig. 2 (a) shows an improved loss measurement setup to enable very high frequency magnetic loss characterization in tens of MHz. It is based on a CPES-developed partial cancellation measurement method, and implements minimized driving and sensing loops and high bandwidth (120MHz) current-sensing probe to facilitate the measurement of very high frequencies. Using this setup, the LTCC and NEC flake magnetic materials are characterized up to 40MHz, and the results are summarized in Fig. 2 (b). The figure shows that the core loss density of LTCC increases dramatically at higher flux density Bm, especially at very high frequencies, while the core loss density change of the NEC flake keeps the same trend (as indicated by the straight lines in Fig. 2 b) as Bm increases.
By comparing the testing results from LTCC and NEC flake materials, we can see that the NEC flake shows advantages over LTCC materials in terms of both permeability and core loss density for very high-frequency IVR applications.
.jpg)
.jpg)


















































































