LIBRARY
Additive Manufacturing of Magnetic Components for Power Electronics Integration
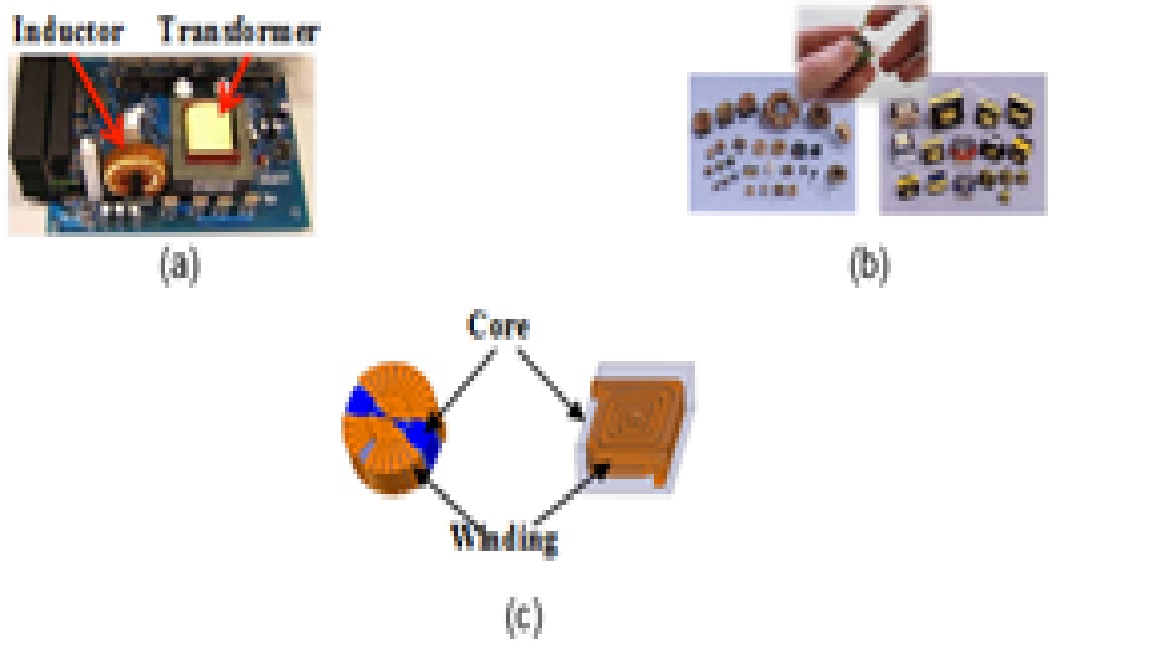
Additive manufacturing (AM) or three-dimensional (3D) printing is a layer-by-layer process of making products and components from a digital model. Its potential has been demonstrated for applications in various industries. Some key benefits of AM are shorter lead times, mass customization, reduced parts count, more complex shapes, less material waste, and lower life-cycle energy use. Recently, some research groups started to explore the application of AM in power electronics. However, so far, we have not found any published work in previous literature that 3D-printed both magnetic and metal materials to form magnetic components. Therefore, the purpose of this work is to explore the feasibility of using a 3D-printing process for fabricating magnetic components.
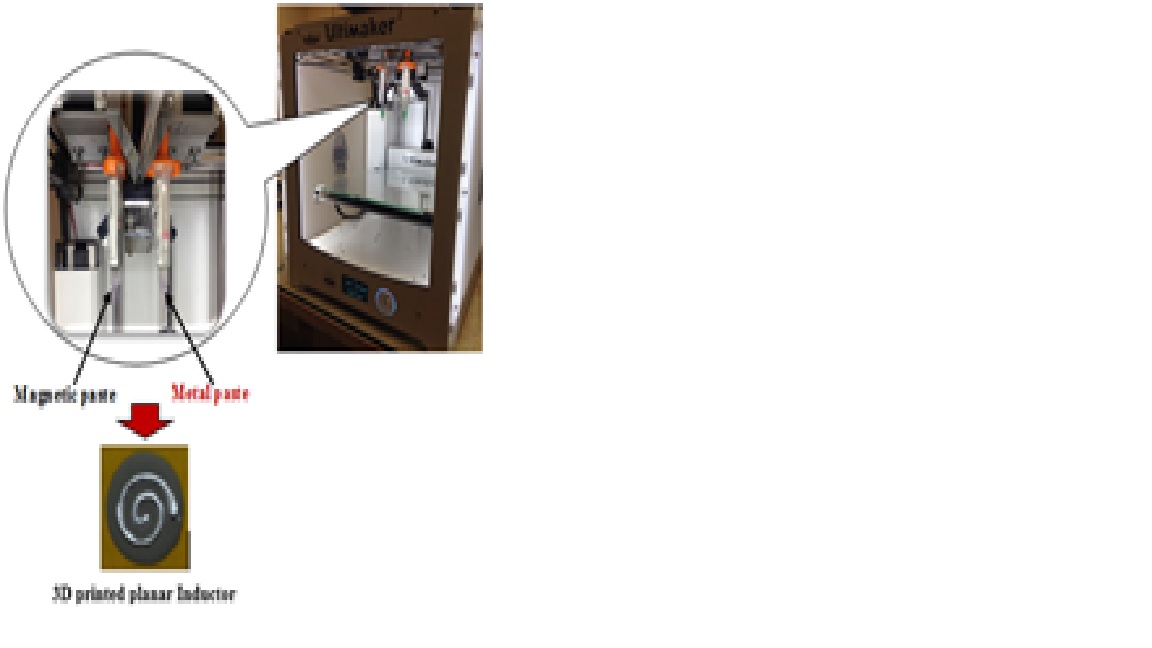
Figure 2 shows that a commercial FDM 3D printer was custom-modified to a two-syringe paste-extrusion 3D printer. Feasibility of the modified 3D printer for fabricating magnetic components was tested. Our patented nanosilver paste was used to serve as a feed material for fabricating the winding of the magnetic components. By extending our prior research experience in the development of the nanosilver paste, a low-temperature (<250°C) curable magnetic paste consisting of a soft magnetic powder and a thermoset polymer called Poly-Mag paste was formulated to serve as a feed material for the magnetic core. The testing structure is a planar core. After the 3D structure of the planar core was fabricated in the printer, it was heated in a programmable muffle furnace to simultaneously cure the polymer in the magnetic core and sinter the nanosilver winding. A finished planar core is also shown in Figure 2.




















































































