LIBRARY
Additive Manufacturing of Toroid Inductors for Power Electronics Applications
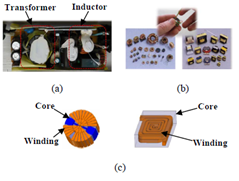
Additive manufacturing (AM) or three-dimensional (3D) printing is a layer-by-layer process of making products and components from a digital model. Some key benefits of AM are shorter lead times, mass customization, reduced part count, ability to manufacture more complex shapes, less material waste, and lower life-cycle energy use. Recently, some research groups have explored the application of AM in power electronics. The purpose of this work is to explore the feasibility of using a 3D-printing process for fabricating magnetic components that consist of both magnetic cores and conductive windings. We chose to work with a multi-material extrusion-based 3D printer because it offers the ease and flexibility of co-processing multiple materials, and for feedstock we can leverage our research expertise in the formulation of pastes of metal and magnetic + poly-mer composites. Use of paste as the feedstock also reduces material waste, lowers the equipment cost, and simplifies the part construction process. The paste-based additive process can be readily scaled up to manufacture a multi-material and multi-functional system. Thus, this process platform offers the potential for further integration of a power electronics circuit by concurrent manufacturing of capacitive, magnetic, and resistive components.