LIBRARY
Design and Multi-Objective Optimization of Coil and Magnetic for Wireless Power Transfer in Auxiliary Power Network
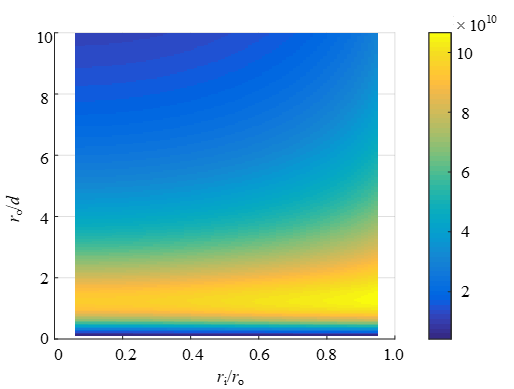
Fig. 1 shows the figure of merit k/Cp, where k is the coupling coefficient presenting the efficiency, and Cp is the coupling capacitance presenting the EMI susceptibility. From the calculation result, the figure of merit has its maximum value ro/d of around one, where ro is the outer radius of the coil and d is the distance between two coils.
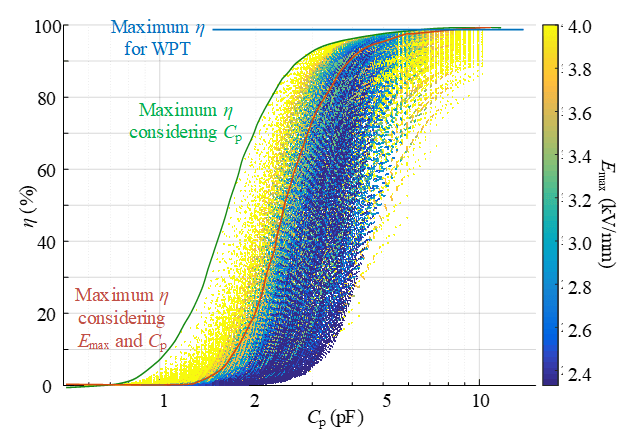
From Fig. 2, for WPT coil optimization, the blue curve shows the normal maximum efficiency that the WPT converter can achieve. The green curve shows the maximum efficiency of WPT as a function of isolation capacitance. In order to minimize the Cp, the very large radius and very small distance between coils should be excluded, which limits the k and efficiency. If insulation capability is considered at the same time, the Pareto-front will be the red curve. For cases where the cable is too thin, the E-field will be too large. Thicker cable can be over-designed for this power level, but it is nec- essary to decrease possible E-field concentration.