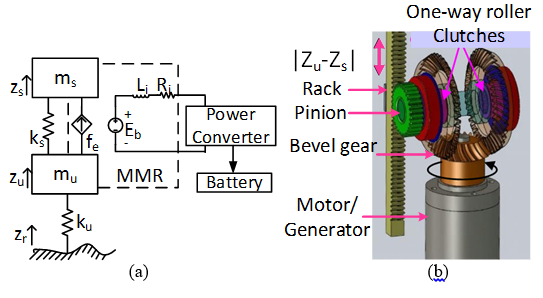
Fig. 1. Quarter car model with mechanical-motion rectifier (MMR) and power converter: (a) Mechanical diagram of suspension system with MMR; (b) Mechanical structure of MMR.
The input current/force of the mechanical-motion rectifier (MMR) can be controlled by using the controller proposed by this paper, and a better passenger experience can be provided with a high-efficiency energy-harvesting suspension system. The nonlinear characteristics from one-way clutches and inertia in MMR induce disengagement and require a large equivalent capacitor, which makes the input current/force of the MMR uncontrollable with a conventional feedback controller design. The controller that has been used in continuous, linear systems cannot be applied in an MMR system. This paper presents an input current/force tracking (ICFT) controller for MMR-based suspension systems. Additional control laws are added in the conventional controller to address the problem of nonlinearity during MMR control. The input current/force of the MMR is controlled to follow the reference signal from the skyhook. The vehicle body displacement is tested by a speedbump on the ground. The displacement error between the skyhook and the ICFT-MMR is within 5%. The total harvested energy is 56 joules, as 56 W of average input power. Equivalent circuits are proven to have identical performances as mechanical models.
In this work, a high-efficiency and reliable energy-harvester - the MMR - is adopted as both an energy harvester and a semi-active shock absorber. To control the regenerative shock absorber, a mechanical-electrical equivalent circuit of the MMR is first introduced. Then an equivalent circuit of a quarter-car model with a skyhook controller (one of the riding comfort controllers) is developed. Next, based on these equivalent circuits, an input current/force tracking controller is proposed and implemented on full-bridge power converter. As a result, the MMR's force can be controlled under its nonlinear and discontinuous characteristics. The controller is constructed based on pulse-width modulation (PWM) control in a power converter, which also functions as an AC-DC converter transferring the energy to the battery. The controller is tested by tracking the reference force from skyhook control to improve riding comfort.
The energy harvesting capability tested in Fig. 3 shows that total harvested energy Ein from the speedbump will be around 56 joules, from which the mean harvested power Pin can be calculated as 56W. Moreover, better riding comfort can be achieved by dynamic controls based on the ICFT controller.
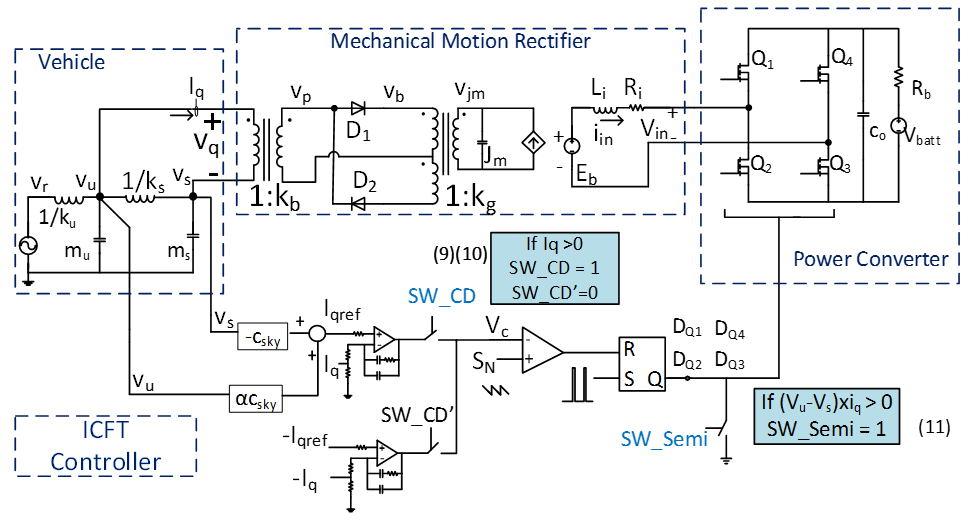
Fig. 2. Input current/force tracking (ICFT) MMR-based suspension system using control laws
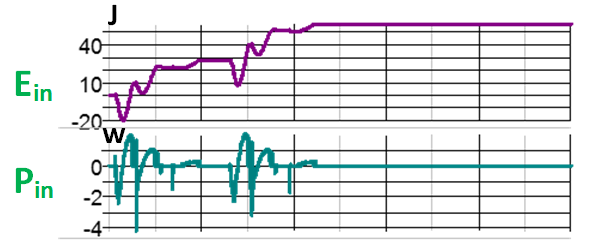
Fig. 3. Impulse response of power converter's input power (Pin) and total harvested energy (Ein).





















































































