LIBRARY
Estimate of Avalanche Breakdown Voltage in 4H-SiC
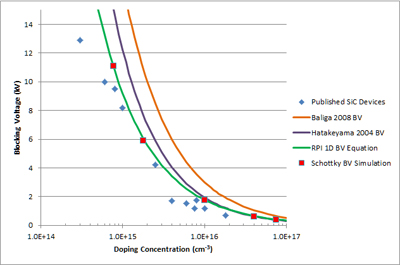
Measured sets of impact ionization coefficients have been published for the 4H-polytype of Silicon Carbide, as well as approximated sets of 1D breakdown equations for calculation of drift layer requirements for design of SiC power devices. This type of equations is useful as a starting point in new device design, and so having accurate analytical equations are important for development of new device structures. Fidelity of these equations with simulation using accepted ionization coefficients and with published experimental device results can be used to compare and contrast the accuracy of these analytical approximations.
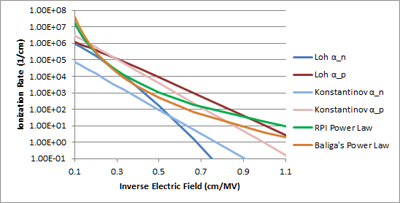
A power law relationship was fit to accepted impact ionization coefficients, as shown in Fig. 1. The fitted equation for ionization rate as a function of electric field is given in equation (1). This relationship approximates the published impact ionization coefficients well for electric fields of 1.5 to 5MV/cm. Solving the ionization integral using this relationship leads to 1D equations (2), (3), and (4).
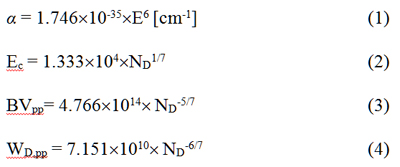
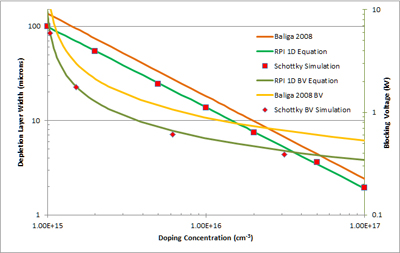
4H-SiC Schottky diodes were simulated with varied doping concentrations, using the Konstantinov impact ionization coefficients. Our equations show strong fidelity to simulation, and published device results (Fig. 2, 3). As expected, physical devices lie slightly below the calculated BVPP due to termination, cell structure, etc. By contrast, other sets of previously published equations overestimate the breakdown voltage by up to 80%.