LIBRARY
Synchronous Generator-based Grid-interface Converter for Energy Storage Systems Integration
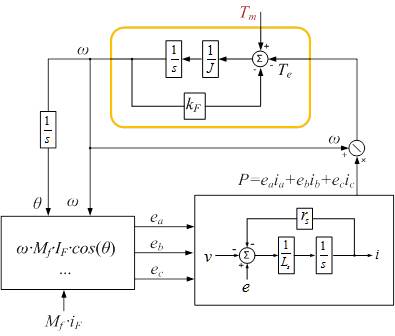
Distributed generation was the rule rather than exception in the early days of electric energy production. Rapid commercialization of the renewable energy sources has resulted in an increased deployment of low, medium and high power distributed generation sources, as well as energy storage (ES) systems. Invariably, renewable DG and ES sources are interfaced to the grid with the assistance of power electronics converters. Fast, digitally controlled converters offer endless possibilities for the most optimal utilization of renewable resources. Moreover, power electronics-based DG can enhance power system controllability due to the fast dynamic response to the power system disturbances and deviations of the voltage and frequency. However, grid-interface converter's phase-locked loops can cause frequency instability in the case when grid output impedance becomes very high, or when there are multiple grid-interface converters connected on the same or adjacent bus with a "weak" link to the strong grid. On the other hand, thousands of synchronous generators work in parallel and share the power with much "milder" interactions in the sense of synchronizing to the grid and to each other. Thus, this paper addresses that issue by showing what features of the synchronous generators operation offer dynamic advantages that could be used in the future for the control of the next generation of grid-interface converters.























































































