LIBRARY
Formal Procedure for Power Electronics Modeling Verification, Validation and Uncertainty Quantification (VV&UQ)
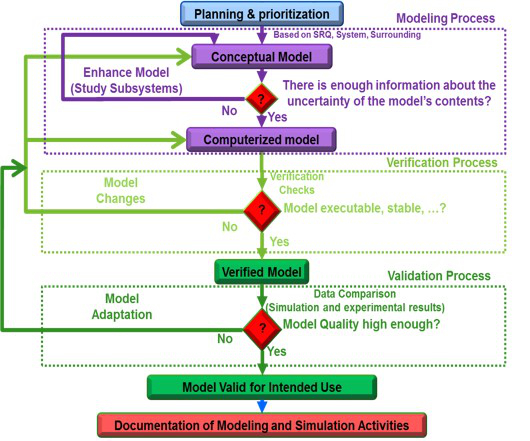
Fig. 1. represents the overview of the proposed VV&UQ formal procedure. The main steps to complete the VV&UQ process are: Planning and Prioritization (P&P), Modeling process, Verification process, Validation process and, at the end, documentation of modeling and simulation activities. Based on the validation metric chosen in this paper, the output of the VV&UQ process is the quantified uncertainty between the simulation and experimental results. The main feature of this procedure is the capability of improving the model until it is valid for intended use.
However, there is a tradeoff between the accuracy of the VV&UQ result and costs. Customers and development teams should decide about their desirable level of accuracy and the costs they are able to afford. These decisions are part of P&P activities. The Modeling Process provides a formulated procedure for building a conceptual model and computerizing it in order to have the most complete model for intended use before starting the V&V process. The verification process first checks the code verification requirements and then calculates the computational error to see whether the model is verified based on the requirements specified in the P&P step. Once the model is verified, the validation process gets started. The Validation Metric is the main part of the validation process, which is the methodology used to quantify the uncertainty between the computational and experimental results. The utilized metric in this paper is based on the Bayesian approach. This method is a statistics method which quantifies the difference between simulation and experimental results based on the intended level of confidence to complete the VV&UQ process. The last but most important is the documentation of the modeling and simulation activities in order to minimize the costs in future projects.






















































































